For more than two thousand years, mankind has tried to solve all the enigmas of this severe dermatosis, but it still remains very unknown. According to statistics, this disease affects from 4 to 7% of the population, women and men are equally susceptible to it. The first signs of psoriasis usually appear during puberty and accompany a person for the rest of his life, then subside and disappear completely, then intensify.
Can psoriasis be cured?Modern medicine has achieved a lot in the treatment of this chronic dermatosis and is able to provide the patient with a decent level of quality of life.
Causes of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory process of the skin, which modern medicine refers to as autoimmune (associated with allergies to its own tissues). There are many causes of psoriasis and factors that predispose to the development of this dermatosis, in connection with which a number of theories of its origin have been presented.
Autoimmune
This is the main theory, as it has been proven that the immune system actively responds to certain types of skin exposure. The skin of people suffering from psoriasis is very sensitive to mechanical, physical and chemical influences. Not only epithelial cells respond to such influences, but the entire immune system.
Cellular immunity is impaired: the ratio between individual subtypes of lymphocytes responsible for the formation of a normal immune response. Thus, in psoriasis, the number of helper T lymphocytes - helpers that regulate immunity - increases, while the number of suppressor T lymphocytes, which suppress an extremely strong immune response, decreases. Lymphocytes and some other cells produce cytokines - active substances that stimulate the immune response. Humoral immunity also suffers, an imbalance of antibodies (immunoglobulins) in the blood serum develops, antibodies to the tissues of the patient's body appear.
Inflammation starts against the background of T lymphocyte activation, but why they are activated has not been proven. In the research process is also the question of how to suppress the autoimmune response without harming the patient.
Exchange
An imbalance in metabolism has a significant effect on the skin and immunity. In patients with psoriasis, there is an acceleration of metabolism, the emergence of a large amount of toxic free radicals and other toxins that support the inflammatory response. Metabolism is concerned:
- protein- CDSN predisposition gene stimulates the synthesis of the protein corneodezmosin, which sensitizes (allergic) the body; the protein content of albumin in the blood decreases and the content of globulins increases; this condition is called dysproteinemia and further increases sensitization;
- fatty- increases the content of lipids and cholesterol in the blood; the use of mainly plant foods and an overall decrease in the calorie content in the daily diet may reduce the activity of psoriatic inflammation;
- carbohydrates- almost always violated;
- exchange of vitamins and minerals- the content of vitamin C in the skin increases, the content of vitamins C, A, B6, B12, iron, copper and zinc in the blood decreases.
Infectious
This theory was important at the beginning and in the middle of the last century. Some bacteria (streptococci), fungi and viruses were considered as causative agents of psoriasis. These theories have not been confirmed. But dermatologists note that any acute infectious process or the presence of a permanent focus of infection can provoke relapses. Viral theory occupies a special place. Recent studies have revealed the effect of retroviruses (viruses containing RNA - HIV, etc. ) on the genetic machinery with the formation of genes for psoriatic predisposition.
genetics
The predisposition to autoimmune reactions is inherited. If a person's loved ones suffer from psoriasis, then the likelihood of developing this disease increases many times over. There are genes for susceptibility to psoriasis (local complexes PSORS1 - PSORS9, PSORS1 is particularly active, contains the genes HLA-C, HLA-Cw6, CCHCR1 and CDSN, which are responsible for the development of the disease). Genes affect metabolism, immunity and the development of autoimmune processes. But the presence of such genes does not guarantee the development of the disease at all. The influence of provocative factors is of great importance.
Neurogenic
Prolonged stress, high neuropsychic stress, disorders of the autonomic nervous system (innervation of the walls of blood vessels and internal organs) can cause the development of psoriasis, causing an imbalance in the endocrine system, impaired metabolic and immunological processes.
Endocrine
Endocrine disorders in psoriasis are common and mainly play the role of a provocative factor. A clear link between the two has not been proven. Dermatologists note that patients often have dysfunctions of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. There are menstrual irregularities in women and sexual function in men.
Symptoms of psoriasis
The main symptoms of psoriasis are skin rashes. But there are other signs. The first manifestations usually appear in adolescence or childhood against the background of hormonal disorders, vegetative-vascular dystonia and prolonged stress.
The disease begins with a feeling of constant fatigue, mood swings. It is characterized by small, pink formations (papules) high above the surface, dusted from above with white skin. They are surrounded by a bright, high edge.
The blush elements grow and combine into large plates with strange shapes. The base of the papule is an inflammatory infiltrate. By the nature of the rash, psoriasis is divided into:
- point- elements with a diameter not exceeding 1 mm;
- teardrops- papules-spots up to 2 mm;
- in coin form- round coins - coins up to 5 mm in size.
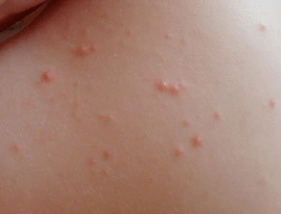
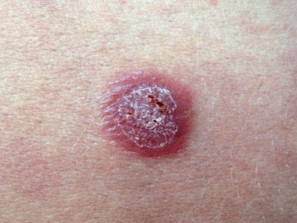
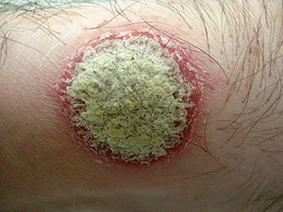
Characteristic features of the rash:
- stain stearin- if scratching, the surface of the papule;
- terminal film- Complete cleaning of the surface of the papule from scales, we will see a transparent film;
- blood dew (Auspitz phenomenon)- after scratching the film and violating its integrity, we will see small bloody spots coming to the surface.
Stages of psoriasis
There are three stages of the disease:
- progressive- the first elements of redness appear, their number increases, all new areas are captured; rashes also appear when you scratch itchy skin or when exposed to certain external irritants (Kebner phenomenon); in the initial stage of psoriasis, the papules begin to clump into large plaques;
- stationary- there are no new elements and those that appeared earlier do not regress;
- regressive- the rash becomes pale, its base becomes less dense; the rash gradually regresses, the process often starting from the central part, so the plates may have the shape of rings; if plaques in psoriasis spread from the periphery to the center, then they simply gradually decrease in size and around them a white ring is formed - the pseudoatrophic edge of Voronov; where there was redness, white, pigmented areas remain - psoriatic leukoderma.
Occasionally, papules are present simultaneously in the skin at all three stages of development. There are also summer and winter forms with a predominance of exacerbations in summer or winter.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Numerous studies have confirmed that this is not a contagious disease. If infectious pathogens participate in its development, then only through a general effect on metabolism, immunity and genetic apparatus.
Patients often ask:
- How does psoriasis spread?
Psoriasis is not transmitted from person to person.
- Is psoriasis inherited?
The answer is again negative, but there is an inherited predisposition in the form of metabolic characteristics and the functioning of the immune system, which is passed on to close relatives.
Types of psoriasis
The nature of the rash, their location, damage to organs and other systems in this chronic dermatosis can be different. According to these signs, several types of disease are distinguished.
Simple (vulgar, slab)
The most common. Its symptoms are papules with a characteristic bright pink color, covered with white scales. Downstream, plaque psoriasis is divided into the following forms:
- easy- if the lesion does not cover more than 3% of the skin; in the progressive stage, the papules grow, but then they quickly undergo a reverse development;
- moderate- rash gets from 3 to 10%; papules are large, clustered;
- heavy- defeat captures more than 10%; the rashes are numerous, merging, forming a wide variety of shapes.
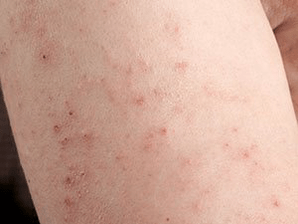
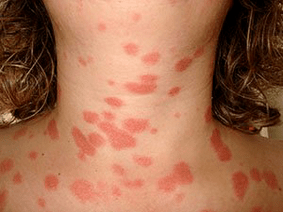
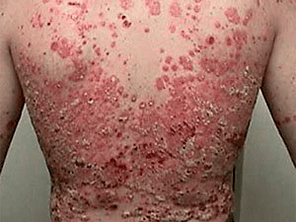
Vulgar psoriasis develops in the form of relapses, alternating with remission, but there is also a continuous course.
Psoriasis of the elbow
This is one of the manifestations of a mild form of plaque inflammation. A distinctive feature of psoriasis on the elbows is the constant presence of one or more "task" plaques on the extensor side of the elbow joints. If these elements are injured, a deterioration begins.
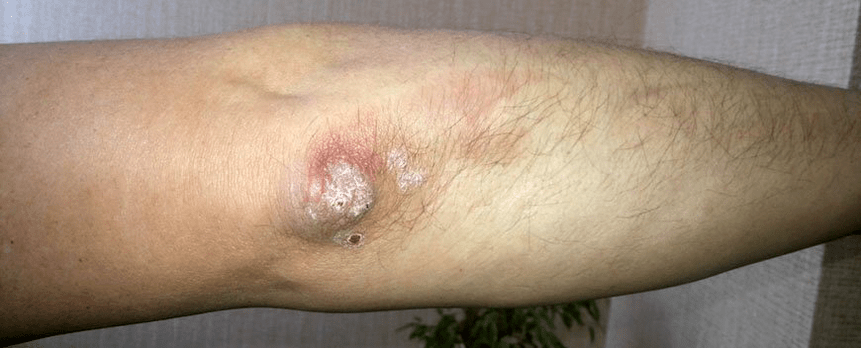
Gutate psoriasis
In the development of guttate psoriasis, bacterial (most often streptococcal) and viral infections are of great importance. Occurs in childhood. Inflammation starts after an infection. Streptococci secrete toxins (antigens - substances foreign to the human body) that bind to tissue proteins. Antibodies are produced against them and autoimmune inflammation develops.
The onset is acute. On the skin of the extremities (rarely the body and face), small red papules appear with a swollen surface. With damage to the redness area, erosions and small sores form, the risk of infection increases.
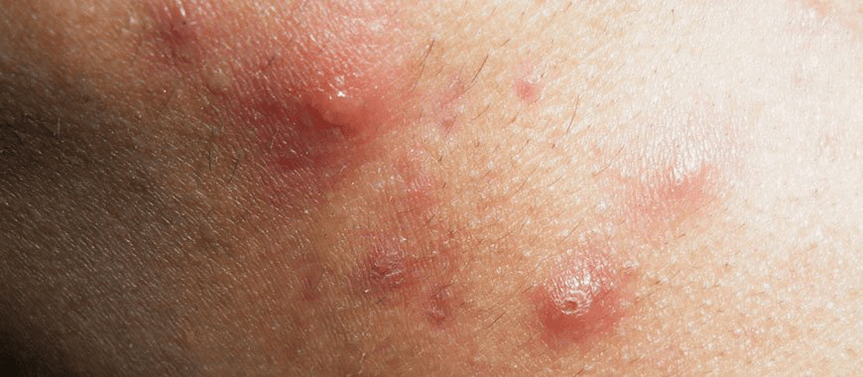
Psoriasis quickly takes on a subacute and chronic course. Relapses are replaced by remission, independent healing or transition to the increased form of the disease is possible.
Palmar-foot psoriasis
It develops in those who do physical work, is accompanied by severe itching and almost always gives a complication to the nails. There are subtypes:
- in the form of a fan in the form of a plate- with large elements on the surfaces of the palm and sole, covered with white scales, which are joined into fan-shaped plates; such psoriasis on the hands is more common;
- circular- ring-shaped scaly elements on the surfaces of the palm and sole;
- horny- is characterized by the growth of thick epithelium with the formation of corns;
A special subgroup is pustular psoriasis on the Barber palms and soles. The areas under the big toe of the extremities are covered with blisters and pustules (with purulent contents), severe itching appears. The abscesses coalesce, then dry out, forming crusts. Elsewhere in the body, characteristic psoriatic elements develop. The disease often spreads to the nails.
Psoriasis of the foot is maintained and worsened by varicose veins, in which case the rash will be mainly in the area of the lower leg.
Psoriasis of the nails
Nail damage can be independent or a complication. Typical symptoms:
- Small holes of different depths appear on the nail plate; similar nail lesions are found in other dermatitis, but in psoriatic lesions they are deeper and less painful when pressed;
- spontaneous slow painless separation of the nail (onycholysis);
- subungual hemorrhage in the toenails, especially if the patient wears tight shoes;
- trakonykia - fogging and irregularities in the nail plate; a depression is formed between the nail and the nail becomes like a spoon (koilonychia).
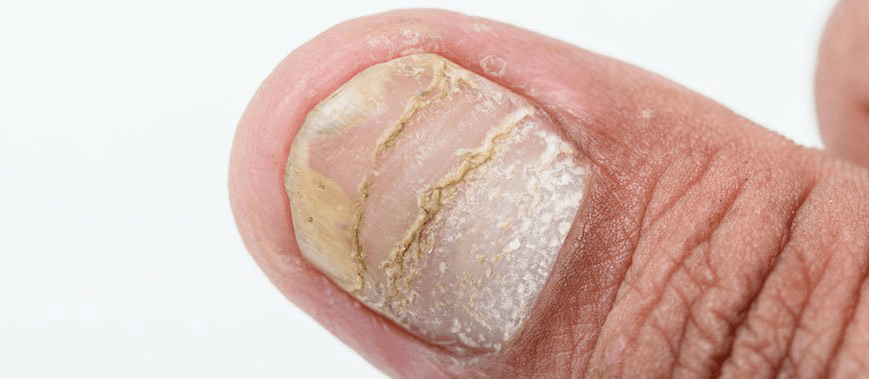
Sometimes the periungual roller is affected by the passage of inflammation to other tissues (psoriatic paronychia).
Psoriasis of the head
Here, the disease proceeds independently or as part of an overall pathological process. It is characterized by leakage, crust formation on parts or the entire surface of the head. Hair growth is not affected at the same time: psoriasis on the head does not impair the function of hair roots. But the leak creates a threat of infection with subsequent damage to the hair follicles.
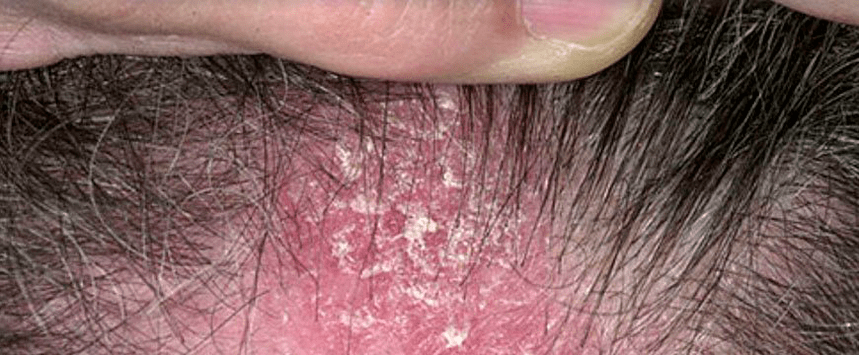
It flows in waves, then subsides with the disappearance of the cortex, then again worsens and is accompanied by severe itching, often leading patients to neurosis.
Seborrheic psoriasis
Seborrhea is a condition caused by a malfunction of the skin glands that produce sebum. A thick oil is produced, irritating the skin and contributing to the development of inflammation - dermatitis.
Seborrheic psoriasis spreads rapidly throughout the head, covering it in the form of a cap and accompanied by severe itching. In the areas behind the ear, sometimes crying develops and an infection joins. The head covered with dandruff and solid crusts sometimes looks like a psoriatic crown.
Psoriasis of the face
Usually, psoriasis on the face is localized in the area of the nasolabial triangle, the eyelids, above the eyebrows, in the areas behind the ear. Melted redness elements form large areas of redness and swelling. If there is a malfunction of the sebaceous glands, the process is often accompanied by crying, crusting and an increased risk of infection.
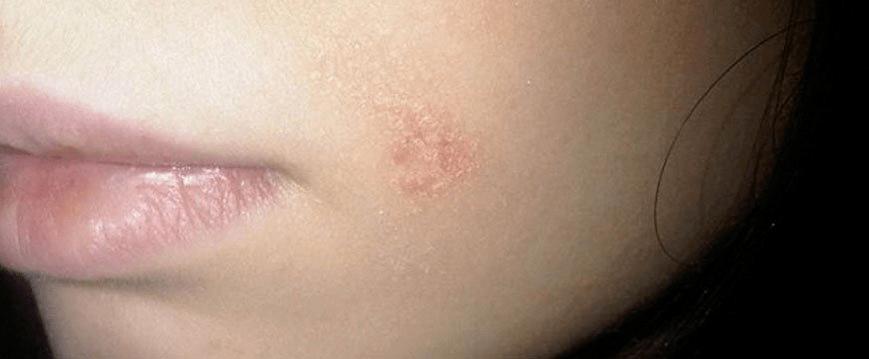
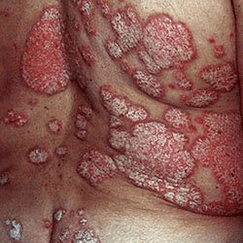
Psoriasis in the genitals
This is not an isolated process. Simultaneously with the defeat of the genitals, there is characteristic psoriatic rash all over the body, so it is not difficult to identify the disease.
Psoriasis on the penis in men and labia majora in women, as well as on adjacent areas of the skin, manifests itself in the form of oval scaly papules, pink slightly raised above the skin. Practically no itching. Sometimes the process spreads to the mucosa and looks like vulvovaginitis in women and balanoposthitis in men.
Atypical psoriatic rashes can be seen in obese people in folds located near the genitals (inguinal, intergluteal). Here, intense red areas with a mirror-like surface form without peeling marks due to constant wetting.
What is the risk of psoriasis and if it should be treated
The risk is that psoriasis can take a severe spread form, the rashes will occupy more than 10% of the ingredient. This stage of the disease is difficult, relapses, rash elements are injured and wet, an infection often joins. Only timely treatment of psoriasis can stop the process of its spread.
Sometimes the disease is complicated by inflammation in the joints with the formation of psoriatic arthritis, against which the function of the joints can be significantly impaired.
Against the background of a systemic autoimmune process, which has a significant effect on the patient's condition, often develop other autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, some types of osteoarthritis, Crohn's disease, etc. ), as well as severe cardiovascular pathology, diseases of the digestive system, neurological reactions.
If you do not start treating psoriasis on time, the patient’s condition will deteriorate dramatically and lead to disability.
There is also a complication such as psoriatic erythroderma, which develops with improper or insufficient treatment of psoriasis, as well as when various irritating factors are exposed to the inflamed skin. The skin acquires a bright pink color with a clear designation of the affected areas by healthy ones, small and large laminate skin. Such a patient requires urgent medical attention.
Is psoriasis treated?
Yes, and quite successfully, but complete recovery can not be guaranteed.

Treatment methods
Autoimmune inflammation requires complex individually selected therapies, lifestyle changes, nutrition, and the elimination of all bad habits. Modern medicine has proposed three basic principles for the successful treatment of psoriasis:
- strict adherence to algorithms for prescribed therapy;
- regular monitoring of therapy effectiveness;
- timely correction of the prescribed therapy with its insufficient effectiveness.
Food for psoriasis
There is no specific diet for psoriasis, but food is of great importance. Therefore, when prescribing a complex treatment, dietary recommendations are necessarily given:
- identify increased body sensitivity to certain foods and exclude them from the diet;
- give preference to fresh vegetables, non-acidic fruits and berries, lean boiled and roasted meat, drink more;
- what not to eat with psoriasis:
- products containing essential oils - onion, garlic, radish;
- beverages containing caffeine (concentrated tea, coffee), alcohol;
- everything is more salty, sour and sweet, rich;
- products that promote sensitization (allergy) of the body - orange fruit, honey, nuts, cocoa, eggs;
- do not eat fatty animal products.

Pegano diet for psoriasis
This diet was developed by the American doctor John Pegano, but has not found official medical recognition. The principle of building the Pegano diet for psoriasis is associated with alkalinization of the body by choosing the right diet. According to this principle, all products are divided into:
- alkali formation (two thirds in the daily diet) - mixtures and juices of non-acidic fruits and berries, vegetables (excluding those that cause increased gas formation);
- acid-forming (one third of the diet) - meat, fish, dairy products, beans, peas, potatoes, cereals, cakes and pastries.
Patients are advised to drink non-carbonated mineral water, drinking water up to 1. 5 liters per day, plus other drunk liquids (compost, juices, etc. )
Drug therapy
Mild psoriasis is treated with topical medications. Severe and rapidly progressing forms of the disease are mainly treated in a hospital setting with the prescription of general (systemic) action drugs.
External treatment of psoriasis
The drug is selected by a dermatologist. For psoriasis vulgaris with dry tightening plates, oils are suitable, if leakage develops (with seborrheic), then creams and medicinal solutions are used. In order to avoid the body's resistance (resistance) to a certain drug, it changes over time.
In the acute (progressive) phase, the following external therapy is performed:
- agents that have a soothing effect - petroleum jelly, 2% salicylic oil;
- non-hormonal oils effective for psoriasis containing activated zinc pyrithione; they suppress infection and have a cytostatic effect (suppress tissue proliferation);
- external agents containing glucocorticosteroid hormones (GCS);
- an agent combined with calcipotriol (an analogue of vitamin D3) and the corticosteroid betamethasone; perfectly suppresses the inflammatory process.
External treatment of inpatient psoriasis:
- oils that dissolve scales (keratolytic) and have an anti-inflammatory effect - 5% naphthalene, boron-naphthalene, tar-naphthalene;
- corticosteroid drugs.
External treatment of psoriasis in the resolution phase:
- the same keratolytic oils, but in a higher concentration: 10% tar-naphthalene oils;
- ointments based on analogues of vitamin D3 - within 6 - 8 weeks; suppresses the inflammatory process and redness of the skin.
For the treatment of psoriasis of the nails, special varnishes are used that suppress the development of the pathological process. It is recommended to treat the periungal phalanges with moisturizing gel.
Systemic treatment of psoriasis
- medicines that relieve inflammation and intoxication - calcium chloride, sodium thiosulfate, unitiol in the form of injections;
- tablets for psoriasis, which suppress the processes of proliferation (proliferation of epithelial cells) - cytostatics that suppress the activity of the immune system, analogues of vitamin A, corticosteroid hormones;
- biological agents containing human IgG class monoclonal antibodies, which act on certain inflammatory bonds by suppressing cytokine synthesis; is a very effective modern medicine that is administered by injection;
- vitamins for psoriasis help restore metabolism and keratinization of epithelial cells; doctors prescribe vitamins A, E, D3, group B.
Folk remedies for psoriasis
Any treatment for psoriasis, including the use of folk remedies, can only be prescribed by a doctor. Self-treatment can lead to the opposite effect: the spread of the disease.
The following methods can be used as part of complex therapy:
- grease- industrial oil processing product; to prepare the oil, you need to buy a solid medical oil at a pharmacy; recipe: in 0, 5 kg of solid oil, add 50 g of honey and half a pack of baby cream; procedures are performed daily; at the pharmacy, you can buy ready-made preparations based on solidol.
- baking soda- a folk remedy for psoriasis, which helps clean the crusts, relieves itching; recipe for soda applications: take 60 g of soda, dissolve in 0. 5 liters of water, soak a gauze cloth in the solution, fold in several layers and apply on the lesion for 20 minutes; after the procedure, clean the skin and put some soothing oil on it; treatment of psoriasis with soda is performed once a day;
- mummy- has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, relieves itching well; can be taken orally once daily, 0. 2 g for two weeks; external therapy is performed with a mummy solution; applied to dry scratching plates twice a day; treatment of psoriasis on the head is performed by rinsing the scalp with a zombie solution after bathing;
- sea salt- relieves inflammation, itching well; sea salt baths: take 1 kg of salt, dilute in two liters of water and add to the bath; take a bath for 15 minutes, then rinse the solution under a warm bath, cleanse the body with a towel and apply a mild oil; treat psoriasis with bath no more than twice a week;
- clay- has a pronounced cleansing effect, absorbing on its surface the toxins formed as a result of inflammation and improper metabolism; helps with drying, eliminating crusts and itching; you can get any mud, but it is better to buy blue mud at a pharmacy; pieces of clay should be well dried, crushed with a hammer, diluted with water and left to stand for several hours; place the resulting clay as a plate on a napkin (up to 3 cm thick) and place on the foci of inflammation for three hours; to Treat Clay Psoriasis Every Other Day |
Important: treatment of psoriasis at home with folk remedies should be carried out carefully and strictly according to the doctor's prescription. Such a treatment will help one patient, while in another it may cause a rapid deterioration and spread of inflammation. Therefore, if, in the background of therapy, the patient's condition has deteriorated, it is necessary to immediately stop and consult a doctor.
Home treatment for psoriasis
When treating psoriasis at home, it is important to follow dietary recommendations, lead a healthy lifestyle, rule out bad habits, and strictly follow all of a dermatologist’s prescriptions.
How to cure psoriasis at home? Some patients try to cleanse themselves of toxins and toxins using all sorts of unconventional methods (enemas, etc. ). This can give the exact opposite result: the work of the digestive tract will break down and a deterioration will begin. Modern medicine recognizes cleansing the body in the form of proper nutrition and getting rid of bad habits.
It is important to follow all doctor's prescriptions and pay attention to how the prescribed therapy works. If it is not effective enough, the doctor will replace the treatment, achieving the maximum therapeutic effect.